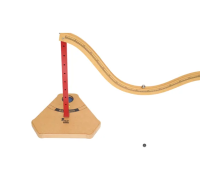
Foundation Physics - Kinetic & Potential Energy Ramp
Description
Foundation Physics - Kinetic and Potential Energy Ramp
- The Foundation Physics range centres around the Universal Stand and includes accessories which allow a wide range of experiments to be conducted. Each add-on includes a comprehensive instructional guide with student tasks which are linked to the curriculum.
When used with the Foundation Physics Universal Stand this Kinetic and Potential Energy Ramp can be used to investigate conservation of energy in relation to a marble rolling up or down a track. A photogate system could be used to measure the time velocity and speed of the marble.
The Kinetic and Potential Energy Ramp includes:
- 1 x Energy Ramp
- 1 x Mounting Bolt
- 1 x Steel Ball (19.11mm)
- 1 x Plastic Ball (19.11mm)
- Instructions
- Teachers Guide
- Student Guide
Additionally required items are:
- Foundation Physics Universal Stand
- Metre Ruler
- Photogate System
- Meter Ruler
Please Note: The Foundation Physics Universal Stand is not included with the Kinetic and Potential Energy Ramp and will need to be purchased separately with code PP00054183.
Pre Orders being taken for September launch.
- Combine with the Foundation Physics Universal Stand (available separately) to teach around and demonstrate Motion and Forces.
- Suitable for staff and student use.
- The Foundation Physics range centres around the Universal Stand and includes accessories which allow a wide range of experiments to be conducted. Each add-on includes a comprehensive instructional guide with student tasks which are linked to the curriculum.
- Key Stage 3 Physics - Speed and the quantitative relationship between average speed distance and time (speed = distanceƒÆ’Įare Ãâ€ÃƒÆ’ÃÆ' · time). Forces being needed to cause objects to stop or start moving or to change their speed or direction of motion (qualitative only)
- Key Stage 4 Physics - Explain the vector-scalar distinction as it applies to displacement velocity and speed. Explain that motion in a circle involves constant speed but changing velocity (qualitative only). Make and interpret measurements of distances times speeds and accelerations and represent these in graphical form.
Activities could include:
- Introduction to the Conservation of Energy
- Conservation of translational energy
- Introduction to energy lost due to friction
- Energy lost due to friction
- Conservation of Mechanical Energy
- Conservation of translational and rotational energy.
Specifications
GB
Physics
Motions & Forces